 |
Innovative Tools
Load Divider
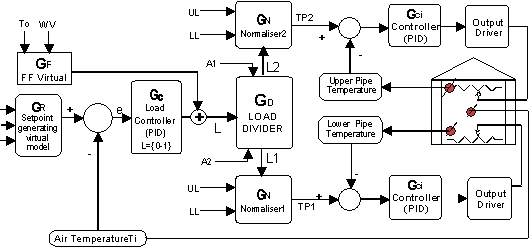
In large space heating spatial temperature differences may become excessive when turbulator funs do not exist. Furthermore in most cases more than one heating systems may exist (i.e. peripheral heating pipes, heating pipes between plant rows, roof heating pipes or roof “fan and coil” system. When two or more such heating systems exist the target is to divide the heating load so as to secure favorable environment at plant’s level (avoid sub_heating to fight the condensation risk but also avoid over_heating to reduce the super_low_humidity risk and consequent water stress) while saving energy.
At IMAG, Holland the experimental greenhouse where Macqu is installed has two heating pipe systems. The Load Divider Macqu method was implemented at the heating system to distribute the desired heating needs to the two heating subsystems. The basic purpose of this method is the smoothing of the temperature distribution from the roof to the bottom of the greenhouse. The secondary purpose of this method is the reduce of the energy heating needs due to the correct distribution of the heating load to the two heating subsystems.
 |
Nested Loop Configuration FF/FBC for Load Sharing with two actuators
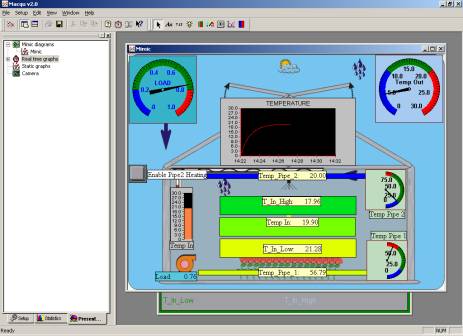 |
View of presentations mimic diagram from the implementation of “Load Divider” method at IMAG.
 |
IMAG greenhouse with the two heating pipes (upper and lower)
Description of the method with multimedia animations