Biological control of vascular plant pathogens
Vascular wilt fungal pathogens cause
widespread, heavy economic losses to a wide range of crops. Fusarium oxysporum and Verticillium dahliae are the major vascular wilt fungi causing
serious economic losses to farmers, as there are no chemical treatments
to control them. Therefore, the use of biocontrol agents (BCAs) is an
appealing control strategy for the conventional and organic farming. In
this frame, a number of different bacterial and fungal isolates are
tested against F. oxysporum and V. dahliae under greenhouse and field conditions. Along their
suppressive activity, the mode of action of the most efficacious isolates
is examined through bioassays, microbiological and elaborate molecular
techniques |
V. dahliae & F. oxysporum - host plant molecular
interaction
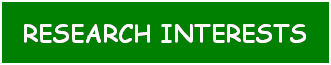
The responses of Arabidopsis
thaliana mutant plants impaired in known pathogen response pathways are used to
explore the plant defence mechanisms deployed against V. dahliae and F. oxysporum. Analysis of the
mutant responses have revealed enhanced resistance in etr1-1 [ethylene receptor
mutant] plants. qPCR analysis showed that V. dahliae vascular colonisation
was reduced in the etr1-1 plants compared to the wt. Furthermore, microarray
experiments indicated that the defence response of etr1-1 plants against V. dahliae is dependent on a set of defence
genes activated upon pathogen invasion |
Plant
pathogens & Food safety
Aspergillus carbonarius and A. niger are the main ochratoxicogenic producing fungi in the Mediterranean
vineyards. The presence of both fungi has been also confirmed in the greek
vineyards. Control strategies include the use of fungicides and biocontrol
agents (yeasts). In a number of published studies, it was shown that the use of
fungicides with cyprodinil+fludioxonil as active ingredients, at veraison
reduces sour rot incidence and Aspergillus sp. on grapes along with ochratoxin A
levels in must. Similarly, an Aureobasidium
pullulans isolate showed to reduce significantly sour rot incidence and
ochratoxin A levels in must |
Molecular identification of plant pathogens
A number of different
Phytophthora isolates from woody and ornamental trees have been characterized on
a molecular basis |
|

|

