-

Financing
EEA 2004-2009 and Hellenic Ministry of Economy and Finance
-

Implemented by
Agricultural University of Athens
-

Head Professor
John Ikonomopoulos
-
Contact
Hit Contact
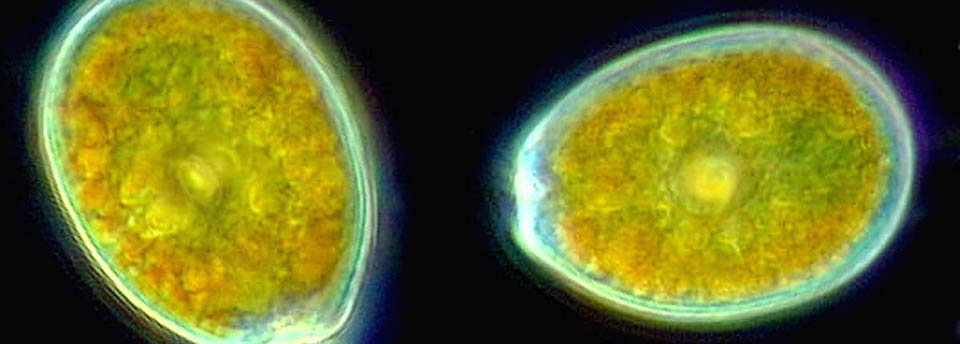
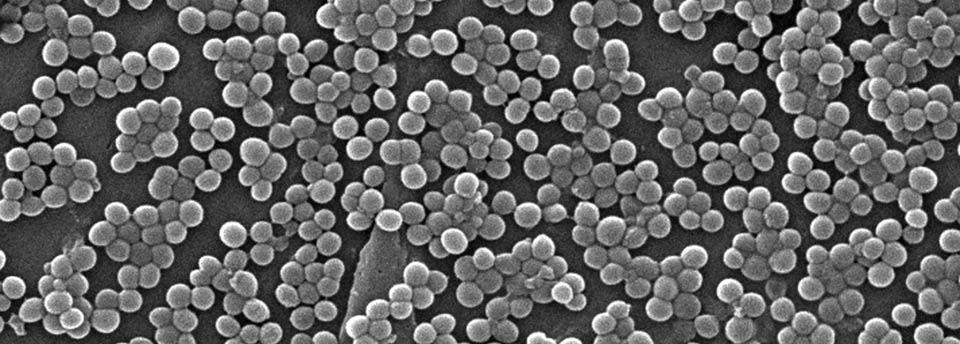
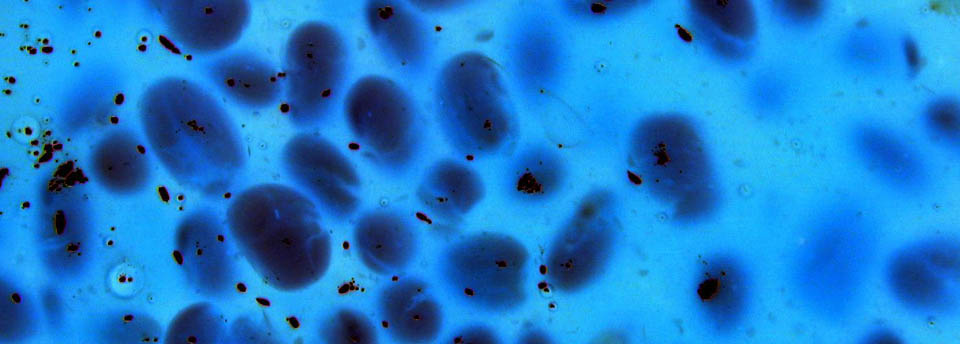
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis
Mycobacterium avium susp. paratuberculosis (MAP) is the causative agent of Johne’s disease in ruminants. MAP has been suggested as a possible cause of Crohn’s disease (CD), a chronic intestinal inflammation of humans. Although this link has not been proved, there is epidemiological evidence that support the causal relationship between MAP and CD. Milk and dairy products have been reported as possible routes for the transmission of MAP to humans. MAP is present in raw milk and can potentially survive the pasteurization process and preservation conditions. This leads to the assumption that it can be present in a viable form in many dairy products. However concern on this issue was raised further in the light of indications that exposure to the specific pathogen even in a non-viable form, may trigger the disease in susceptible individuals in a pattern similar to that of an allergic reaction. Unfortunately conclusive evidence on the potential association of MAP with CD will not be easily made available in the near future. Precautionary measures are suggested by many regulatory and national authorities, since a higher level of alert cannot be officially and scientifically justified.