-

Financing
EEA 2004-2009 and Hellenic Ministry of Economy and Finance
-

Implemented by
Agricultural University of Athens
-

Head Professor
John Ikonomopoulos
-
Contact
Hit Contact
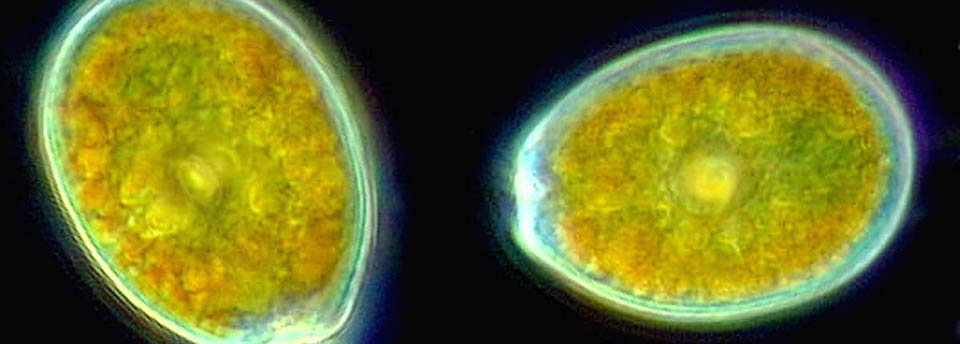
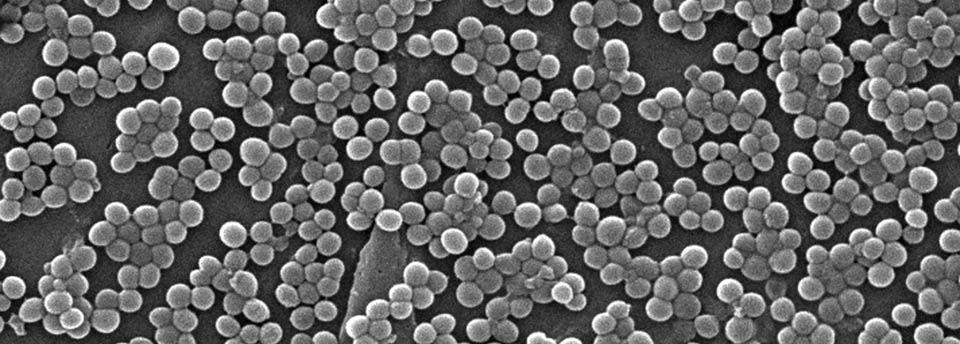
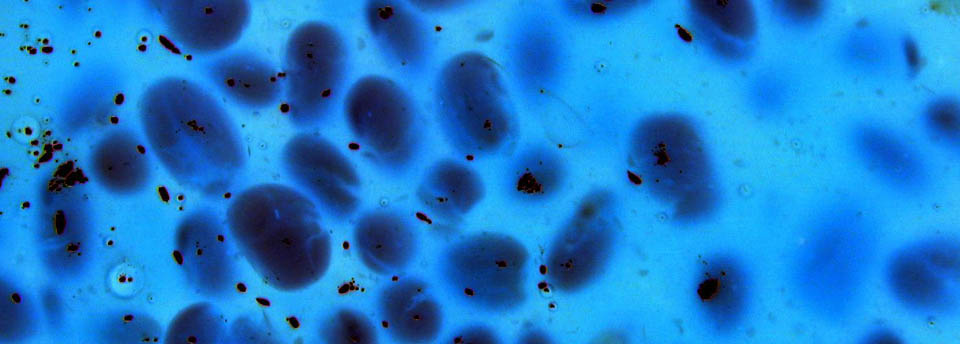
Salmonella spp
Salmonellosis is a food borne disease caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella. The most common serotypes of the pathogens are Enteritidis and Typhimurium. Salmonella may be transmitted among people, animals and birds but the majority of human infections are caused by the consumption of contaminated food. Most common form of infection is gastro-enteritis. Groups in high risk of infection are infants and the elderly. Symptoms usually appear 12-72 hours post ingestion and include fever profuse diarrhea and vomiting leading to dehydration that in some cases may be fatal. In high risk groups the bacterium may enter the blood stream and thus cause meningitis, osteitis, abscesses etc. In nature the pathogen is mainly found in the intestinal tube of animals (commonly cattle and sheep) and birds. Raw meat, poultry, shellfish, eggs and egg products, milk and raw cheese are common sources of the bacterium.